Dongfeng Gu
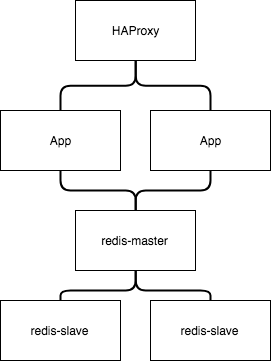
Docker example: application hub with 6 containers
- 4 minsThe basic structure of these docker hub
Comand need to run
1. Initialize the all the container node
# 1. pull the docker images
docker pull ubuntu
docker pull django
docker pull haproxy
docker pull redis
# Note: start the nodes in the following sequence
# redis-master -> redis-slave -> APP -> HAProxy
# 2. start the redis container
docker run -it --name redis-master redis /bin/bash
docker run -it --name redis-slave1 --link redis-master:master redis /bin/bash
docker run -it --name redis-slave2 --link redis-master:master redis /bin/bash
# 3. start the Django container
docker run -it --name APP1 --link redis-master:db -v ~/Projects/Django/App1:/usr/src/app django /bin/bash
docker run -it --name APP2 --link redis-master:db -v ~/Projects/Django/App2:/usr/src/app django /bin/bash
# 4. start the HAProxy container
docker run -it --name HAProxy --link APP1:APP1 --link APP2:APP2 -p 6301:6301 -v ~/Projects/HAProxy:/tmp haproxy /bin/bash
2. Configure redis-master container
# get the container id
docker ps
# inspect the mounted volume of the redis-master container
docker inspect --format "{{ .Volumes }}" <redis-master-id>
# go to the corresponding folder in your host machine
cd /var/lib/docker/vfs/dir/<id>
cp <your-own-redis-dir>/redis.conf redis.conf
# edit the redis configuration file
vi redis.conf
# modify the following settings
# daemonize yes
# pidfile /var/run/redis.pid
# login your container
docker attach <redis-master-id>
# copy the redis configuration file to the executing folder
# and run the redis server
cd /data
cp redis.conf /usr/local/bin
cd /usr/local/bin
redis-server redis.conf
3. Configure the redis-slave containers ( do the following command for both containers )
# inspect the mounted volume of both redis-slave containers
docker inspect --format "{{ .Volumes }}" <redis-slave-id>
# go to the corresponding folder in your host machine
cd /var/lib/docker/vfs/dir/<id>
cp <your-own-redis-dir>/redis.conf redis.conf
vi redis.conf
# change the following settings
# daemonize yes
# pidfile /var/run/redis.pid
# slaveof master 6379
# login your container
docker attach <redis-slave-id>
# copy the redis configuration file to the executing folder
# and run the redis server
cd /data
cp redis.conf /usr/local/bin
cd /usr/local/bin
redis-server redis.conf
4. Redis container test
# login redis-master container
docker attach <redis-master-id>
# login redis client
redis-cli
# store one data
... > set master testdata
OK
... > get master
"testdata"
# login redis-slave container
docker attach <redis-slave-id>
# login redis client
redis-cli
... > get master
"testdata"
5. Configure Django ( configure for both apps )
# login the Django container
docker attach <app1-id>
# install python redis support
pip install redis
# build the app
cd /usr/src/app
mkdir dockerweb
django-admin.py startproject redisweb
cd redisweb/
python manage.py startapp helloworld
# exit the container
<Ctrl + D>
# go to the link folder in your host machine
cd ~/Projects/Django/App1
# change the vide file of helloworld application
cd dockerweb/redisweb/helloworld/
sudo su
vi views.py
######################################################
# views.py
# from django.shortcuts import render
# from django.http import HttpResponse
# import redis
# def hello(request):
# str=redis.__file__
# str+="<br>"
# r = redis.Redis(host='db', port=6379, db=0)
# info = r.info()
# str+=("Set Hi <br>")
# r.set("Hi", "HelloWorld-APP1")
# str+=("Get Hi: %s <br>"" % r.get('Hi'))
# str+=("Redis Info: <br>")
# str+=("Key: Info Value")
# for key in info:
# str+=("%s: %s <br>" % (key, info[key]))
# return HttpResponse(str)
#
######################################################
# edit the redisweb setting file
cd ../redisweb/
vi setting.py
######################################################
# add the following to the INSTALLED_APPS section
#
# INSTALLED_APPS = (
# 'django.contrib.admin',
# 'django.contrib.auth',
# 'django.contrib.contenttypes',
# 'django.contrib.sessions',
# 'django.contrib.messages',
# 'django.contrib.staticfiles',
# 'helloworld',
# )
######################################################
# edit the urls.py file in the project
vi urls.py
######################################################
# from django.conf.urls import patterns, include, url
# from django.contrib import admin
# from helloworld.views import hello
# urlpatterns = patterns('',
# url(r'^admin/', include(admin.site.urls)),
# url(r'^helloworld$', hello),
# )
######################################################
# enter the app container
docker attach <app1-id>
# complete the project
cd /usr/src/app/dockerweb/redisweb
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py syncdb
# start the server, note that app2 should have port 8002
python manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8001
6. Configure the HAProxy container
# enter the folder in your host
cd ~/Projects/HAProxy
vi haproxy.cfg
######################################################
# global
# log 127.0.0.1 local0
# maxconn 4096 # maximum connection
# chroot /usr/local/sbin # change the current work directory
# daemon # run the program as daemon
# nbproc 4 # number of HAProxy instances
# pidfile /usr/local/sbin/haproxy.pid # pid file location
# defaults
# log 127.0.0.1 local3
# mode http
# option dontlognull
# option redispatch
# retries 2
# maxconn 2000
# balance roundrobin
# timeout connect 5000ms
# timeout client 50000ms
# timeout server 50000ms
# listen redis_proxy 0.0.0.0:6301
# stats enable
# stats uri /haproxy-stats
# server APP1 APP1:8001 check inter 2000 rise 2 fall 5 # your APP1 container
# server APP2 APP2:8002 check inter 2000 rise 2 fall 5 # your APP1 container
######################################################
# login the HAProxy container
docker attach <haproxy-id>
cd /tmp
cp haproxy.cfg /usr/local/sbin/
cd /usr/local/sbin/
haproxy -f haproxy.cfg
# note that we need to kill the haproxy process if
# we make some changes in the configuration file
apt-get install psmisc
killall haproxy
Access the http://
Check the status of haproxy by http://